Smart Info About How To Decrease Antibiotic Resistance

Since the resistance to the first commercial antimicrobial agent (penicillin) was.
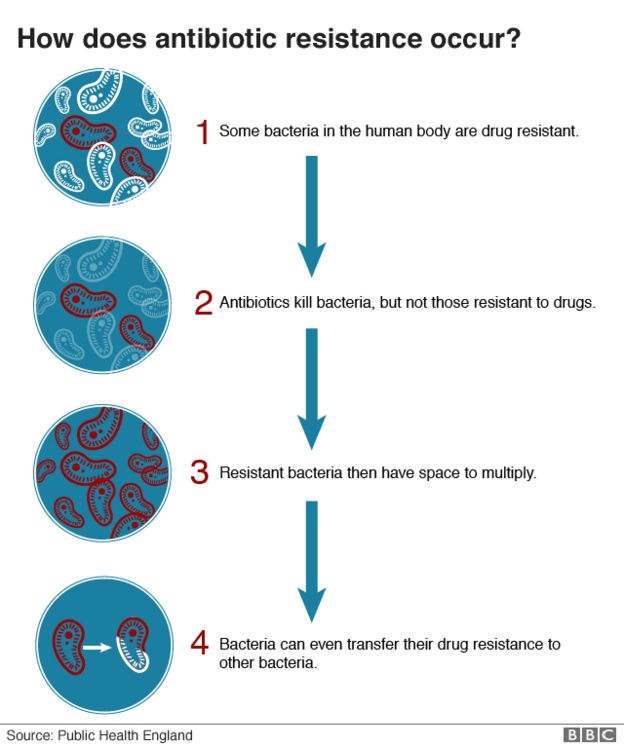
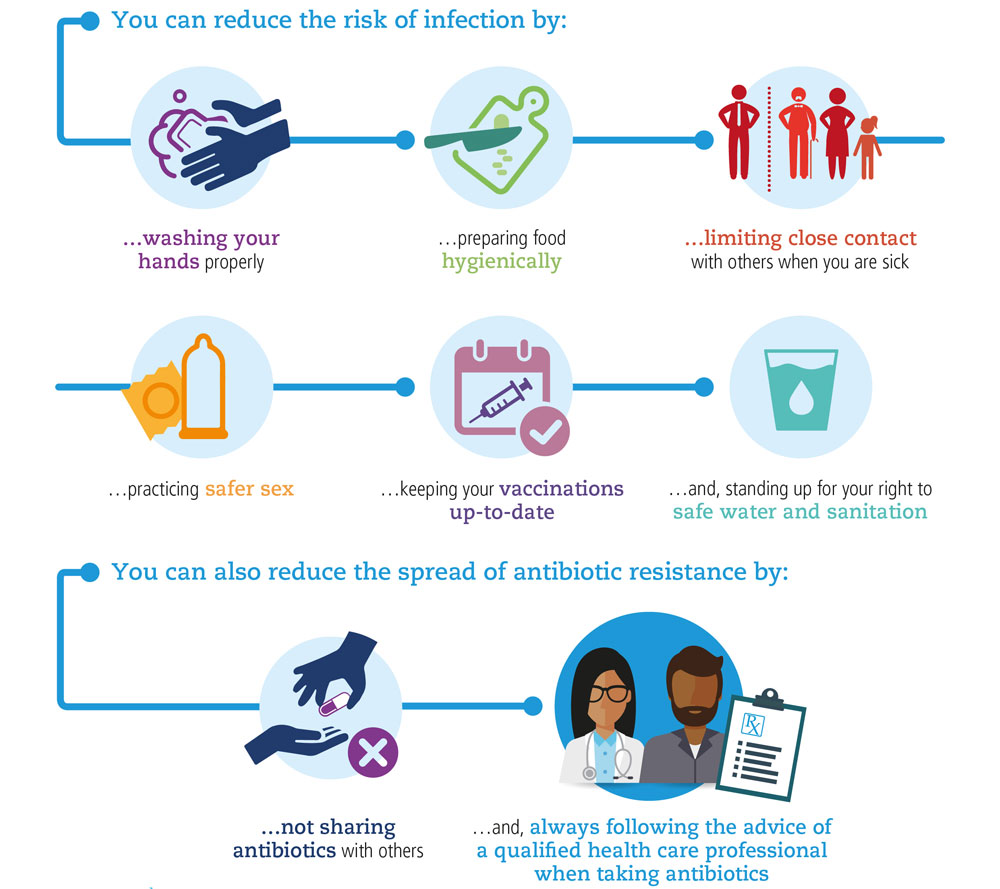
How to decrease antibiotic resistance. Here are five priorities for combating antibiotic resistance in 2020: Reduce antibiotic use in human medicine. These include vaccination, implementing hand hygiene and responding rapidly to unusual genes and germs when they first appear.
Prevent infections in the first place improve antibiotic and antifungal use to slow the development of resistance stop the spread of resistance when it does develop Pcast’s 3 key recommendations: Cresomycin, the new antibiotic, is synthetic.
In 2020, hospital administrators, accrediting organizations, and policymakers should focus on enhancing the quality of hospital antibiotic stewardship programs, which aim to ensure appropriate antibiotic use and patient safety. Antimicrobial agents have been greatly important cornerstones of clinical medicine since the second. Fda combating antibiotic resistance through activities that include approval of certain new antibiotics.
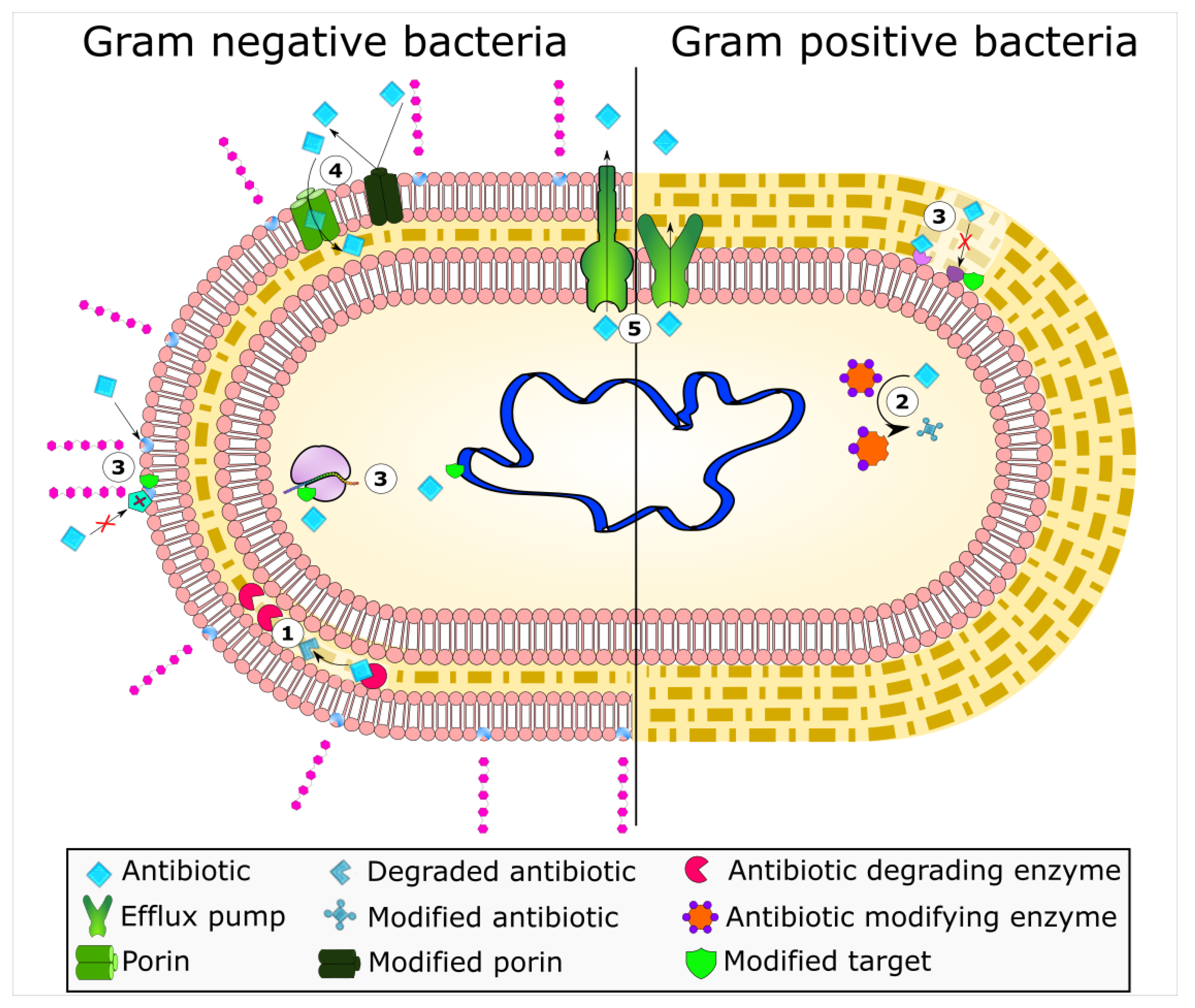
International, national and local approaches have been advised for control and prevention of antimicrobial resistance. Evidence of the current system’s failure is the drastic decrease in. They work either by killing off the bacteria or preventing the bacteria from reproducing.
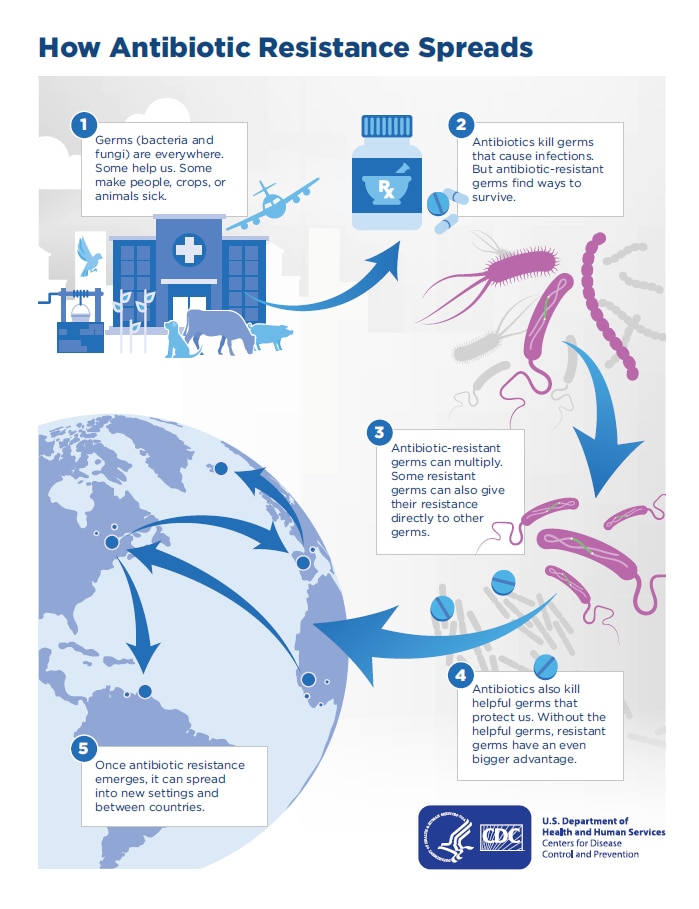
How we can stop antibiotic resistance 7 june 2017 by erin biba features correspondent antibiotic resistance it’s been dubbed “the end of modern medicine”. Antibiotic resistance has spread around the world, and it's making some diseases, such as meningitis or pneumonia, more difficult to treat. It also highlights the eu’s commitment to the one health approach, safeguarding both animal and global public.
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt or evolve to survive antibiotic treatment. The global rise in antibiotic resistance poses a significant threat, diminishing the efficacy of common antibiotics against widespread bacterial infections. When bacteria no longer respond to antibiotics, treatment is more costly and burdensome and is much less likely to.
The 2022 global antimicrobial resistance and use surveillance system (glass) report highlights alarming resistance rates Even though we have a very large number of antimicrobial agents from which to choose for potential infection therapy, there is documented antimicrobial resistance to all of these, and this resistance occurs shortly after. Since 2015, fda approved new antibiotics that can treat certain resistant bacteria.
The fourth joint report on integrated analyses of amc was published yesterday in the efsa journal by the european centre for disease prevention. This is a big issue as it can cause antibiotics to become less effective. People receiving health care or those with weakened immune systems are often at higher risk for getting an infection.
Causes of the global resistome are overpopulation, enhanced global migration, increased use of antibiotics in clinics and animal production, selection pressure, poor sanitation, wildlife spread, and poor sewerage disposal system. For example, if every child in the world received a vaccine to protect them from infection with streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria (which can cause pneumonia, meningitis and middle ear infections), this would prevent an estimated 11. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) is one of the most significant public health threats faced in this century 1.the global challenge to address amr has prompted studies to better ascertain its.
Sepsis how antibiotic and antifungal use affects resistance antibiotics and antifungals save lives, but their use can contribute to the development of resistant germs. Curbing antibiotic use works. The subsequent decrease in the ph could be explained by the strengthening of microbial nitrification,.